- Home
- Products
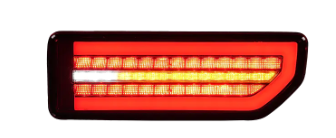
- Tail Lamp for TOYOTA Series
- Tail Lamp for HONDA Series
- Tail Lamp for TESLA Series
- Tail Lamp for CHEVROLET Series
- Tail Lamp for BUICK Series
- Tail Lamp for MAZDA Series
- Tail Lamp for VOLKSWAGEN Series
- Tail Lamp for NISSAN Series
- Tail Lamp for SUZUKI Series
- Tail Lamp for FORD Series
- Tail Lamp for HYUNDAI Series
- Tail Lamp for RENAULT Series
- About Us
- News
- Contact

 English
English русский
русский Español
Español